|
Data Asset Class
|
A category of data being described, such as a data asset, data product or data exchange.
|
|
Purpose
|
This attribute differentiates data sets that comprise the agency’s data inventory according to the level of development applied to the data, and the level of re-useability of the data.
|
|
Additional comments
|
The data asset class makes clear the breadth of use cases for an item using language consistent across government data inventories, and to ensure contributions to the Australian Government Data Catalogue (AGDC) are fit for purpose.
|
|
Obligation
|
Mandatory
|
|
Controlled values
|
Select and record a single value from the options provided:
- Data, e.g. raw data stored in transactional systems such as Centrelink ISIS, Child Support Cuba, Medicare Mainframe. Data may be extracted and prepared for further use in other systems.
- Dataset, e.g. data extracted for use with minimal or no development, such as copies of source data landed in the EDW or Data Lake.
- Data Asset, e.g. curated data that has been prepared and developed in some way for effective use, such as curated datasets and data marts.
- Data Product, e.g. transformed data with a high level of development for a specific purpose, such as MI/OI reports and data dashboards or visualisations.
- Data Exchange, i.e. identifies the record as a data exchange, as registered in CITADEL. A Data Exchange will be the parent record for one or more Data Exchange Transfers.
- Data Exchange Transfer, i.e. identifies the record as a data exchange transfer, as registered in CITADEL. It must be connected to a parent Data Exchange record and describes the specific data shared with an exchange partner.
- Dataset Subset, i.e. a logical grouping of tables within a large database. It enables the creation of a hierarchy of child datasets within a parent dataset.
|
|
Example(s)
|
Data Asset:
|
Data Product
|
|
Data Exchange:
|
Data Exchange
|
|
Data Transfer:
|
Data Exchange Transfer
|
|
|
Data Granularity
|
The lowest level of detail or data granularity which is available in the data.
|
|
Purpose
|
This attribute enables users to find, categorise and evaluate the fitness of the data to their needs, and understand implications for the appropriate management of that data.
|
|
Additional comments
|
Where the data contains multiple levels of granularity, such as aggregate data and unit record data, select multiple values accordingly.
|
|
Obligation
|
Data Asset:
|
Optional
|
|
Data Exchange:
|
Optional
|
|
Data Transfer:
|
Mandatory
|
|
Controlled values
|
Record one or more values from the options provided - select the Plus (+) button to browse and add values. Where a desired value is not listed contact metadata.management.
- Person unit record sensitive identifiable.
- Person unit record identifiable.
- Person unit record de-identified.
- Unit record non-personal information.
- Aggregate (e.g. summary information / performance measures)
|
|
Example(s)
|
- Person unit record sensitive identifiable
|
|
|
Purpose
|
The intentions or purposes for which an item was developed and how an item is to be used.
|
|
Purpose
|
This attribute provides additional business context by describing the purpose for collecting, creating, receiving or otherwise holding data, ensuring data is used as intended, and supports compliance with the Privacy Code.
|
|
Additional comments
|
The purpose field is used in conjunction with the Definition and Keywords for identifying and describing the purpose for which the information was collected and is required for all items that contain personal information. This is required under the Australian Government Agencies Privacy Code requirement for agencies to maintain records of personal information holdings. This information ensures the agency is aware of all the personal information it handles, where it is kept and the risks associated with that information.
|
|
Obligation
|
Data Asset:
|
Mandatory
|
|
Data Exchange:
|
Mandatory
|
|
Data Transfer:
|
Not included
|
|
Controlled values
|
The purpose should typically be 2-3 sentences or dot points which explain how data is used.
|
|
Example(s)
|
The power BI dashboard is used and maintained for the purposes of:
- collecting and maintaining a record of new staff employed by the agency,
- providing SES oversight of workforce status, attrition and new hire volumes,
- supporting adherence to the ASL staffing cap by recording over or under spending,
- informing SES when undertaking recruitment activities,
- contributing to financial year reporting requirements, and
- registered ICT user account creation.
|
|
|
Keywords
|
Standardised terms that describe the subject matter of the data.
|
|
Purpose
|
This attribute is used to describe topics covered by the data, using language consistent across government data inventories. It answers the question “what is in this data?” and supports data discovery
|
|
Additional comments
|
The keywords field is used in conjunction with the Definition and Purpose for identifying and describing an item. Terms are selected from the Australian Government Interactive Functions Thesaurus (AGIFT) and internal agency business terminology.
When selecting keywords, consider what search terms your users may choose when searching for the item, and provide as much granularity as practicable.
Contact metadata.management to add additional keywords to the list. A full list of AGIFT terms are published on the National Archives of Australia (NAA) website.
|
|
Obligation
|
Data Asset:
|
Mandatory
|
|
Data Exchange:
|
Mandatory
|
|
Data Transfer:
|
Optional
|
|
Controlled values
|
All records must contain at least one AGIFT high-level function term and one of the following keywords to indicate whether an item is:
- Program data: data captured specifically for the purpose of administration and payments for programs across social welfare, child support, health, veterans and aged care sectors. For example, customer/patient circumstances data.
- Operational performance data: data that enables or supports the delivery and assurance of the internal services that are required to operate programs. For example, phone statistics, service officer statistics, claim/processing statistics.
- Corporate workforce data: data about the agency itself and its employees.
Additional terms can be included in or selected from AGIFT - Additional terms, All glossary terms; or new terms submitted as free text in this field.
|
|
Example(s)
|
Data Asset:
|
Corporate workforce data, Workforce (employee, labour hire), Indigenous affairs, Workplace discrimination monitoring
|
|
Data Exchange:
|
Program data, Data exchange, Customer circumstances, Timeliness, Accuracy, Income, Assets, Department of Social Services (DSS)
|
|
|
Asset Population
|
A explanation of the demographic coverage of the data asset.
|
|
Purpose
|
This attribute provides details describing who the data is about.
|
|
Additional comments
|
The field provides crucial context to support safe and ethical use of the data.
|
|
Obligation
|
Optional
|
|
Controlled values
|
At least one complete sentence.
|
|
Example(s)
|
All people over the age of 45 who receive Job Seeker payment.
|
|
|
Legal Authority
|
The legal mandates under which an item was collected, created, received or used.
|
|
Purpose
|
This attribute established the legal authority, or authorities are used to classify an item according to its governing legislation, streamlining action to ensure its compliance
|
|
Additional comments
|
The legal authority may include Memorandum of Understanding (MoU); Legislation; Machinery of Government (MoG); Government policies or acts. It may also include the authority, e.g. (Australian Government) Federal Register of Legislation or Data Availability and Transparency Act 2022.
|
|
Obligation
|
Data Asset:
|
Mandatory
|
|
Data Exchange:
|
Mandatory
|
|
Data Transfer:
|
Not included
|
|
Controlled values
|
Record one or more values from the options provided - select the Plus (+) button to browse and add values. Where a desired value is not listed contact metadata.management.
- Centrelink: A New Tax System (Family Assistance) (Administration) Act 1999, Aged Care Act 1997, Australian Hearing Services Act 1991, Dental Benefits Act 2008, Disability Services Act 1986, Human Services (Centrelink) Act 1997, Paid Parental Leave Act 2010, Social Security (Administration Act) 1999, Student Assistance Act 1973
- Child Support: Child Support (Registration and Collection) Act 1988, Child Support (Assessment) Act 1989
- Medicare: Australian Immunisation Register Act 2015, Healthcare Identifiers Act 2010, Health Insurance Act 1973, Human Services (Medicare) Act 1973, Medical Indemnity Act 2002, Midwife Professional Indemnity (Commonwealth Contribution) Scheme Act 2010, National Health Act 1953, Private Health Insurance Act 2007
- Governance and Regulation: Privacy Act 1988, Freedom of Information Act 1982, Public Governance, Performance and Accountability Act 2013, Public Service Act 1999, Fair Work Act 2009, Taxation Administration Act 1953, Australian Prudential Regulation Authority Act 1998
|
|
Example(s)
|
- Social Security (Administration Act) 1999
- Public Governance, Performance and Accountability Act 2013
|
|
|
Sharing Authority
|
The legal mandate or data sharing arrangement under which the data can be supplied.
|
|
Purpose
|
This attribute identifies the document or documents providing authority for data to be shared or published and the documents which detail arrangements under which data is exchanged.
|
|
Additional comments
|
The sharing authority should reference documents such as:
- Specific acts/sections of legislation
- Public Interest Certificate (PIC)
- Public Data Sharing Protocols
- Bilateral agreements or Contracts
|
|
Obligation
|
Data Asset:
|
Optional
|
|
Data Exchange:
|
Mandatory
|
|
Data Transfer:
|
Not included
|
|
Controlled values
|
Adhere to legal material referencing conventions, as per the Australian Government Style Manual.
|
|
Example(s)
|
- Services Schedule for Data Sharing (2025)
|
|
|
Security Classification
|
The Protective Security Policy Framework (PSPF) security classification applied to the data.
|
|
Purpose
|
This attribute ensures data is handled, communicated, disclosed and stored appropriately and relates to the Sensitive Data and Rights attributes.
|
|
Additional comments
|
Specify the classification appropriate for the data, taking into consideration whether the data contains personal or sensitive information. If data contains multiple components, record the highest security classification.
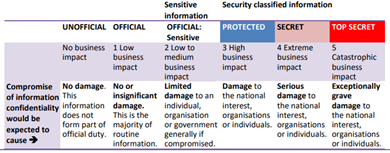
For further information, refer to the agency’s Security Markings intranet page.
|
|
Obligation
|
Data Asset:
|
Mandatory
|
|
Data Exchange:
|
Mandatory
|
|
Data Transfer:
|
Not included
|
|
Controlled values
|
Select and record a single value from the options provided:
- UNOFFICIAL, OFFICIAL, OFFICIAL: Sensitive, PROTECTED, SECRET, TOP SECRET.
|
|
Example(s)
|
|
|
|
Sensitive Data
|
The type of sensitivity of the data asset, where applicable.
|
|
Purpose
|
This attribute alerts users to protections and procedures required during access, storage, transport, and disposal of the data.
|
|
Additional comments
|
The Privacy and Secrecy hub provides sensitive data information, definitions and resources
|
|
Obligation
|
Data Asset:
|
Mandatory
|
|
Data Exchange:
|
Not included
|
|
Data Transfer:
|
Mandatory
|
|
Controlled values
|
Record one or more values from the options provided - select the Plus (+) button to browse and add values. Where a desired value is not listed contact metadata.management.
- N/A (not sensitive): no sensitive data is contained within an item.
- Personal privacy: restrictions on access to, or use of, personal information collected for which can be used to identify an individual.
- Legal privilege (including commercial-in-confidence): restrictions on access to, or use of, information covered by legal privilege.
- Legislative secrecy: restrictions on access to, or use of, information covered by secrecy provisions.
|
|
Example(s)
|
|
|
|
Personal or Sensitive Information Details
|
Additional description of any personal or sensitive information contained in the data.
|
|
Purpose
|
This attribute provides further details regarding any personal or sensitive information contained in the data to enable identification and retrieval of assets which contain different types of personal or sensitive information.
|
|
Obligation
|
Data Asset:
|
Conditional (Mandatory if item classification is OFFICIAL: Sensitive)
|
|
Data Exchange:
|
Not included
|
|
Data Transfer:
|
Conditional (Mandatory if item classification is OFFICIAL: Sensitive)
|
|
Controlled values
|
Record one or more values from the options provided - select the Plus (+) button to browse and add values. Where a desired value is not listed contact metadata.management.
- Personal data: Name, Date of birth, Address, Phone and contact details, Bank details, Employment details, Gender, Personal identifiers, Personal identifiers (Customer), Personal identifiers (Staff), Proof of identity documents, Relationship details, Services applied for or received, Voice recordings.
- Sensitive data: Biometric information, Biometric templates, Criminal record, Genetic information, Health information, Indigenous status, Racial or ethnic origin, Membership of a political association, Membership of a professional or trade association, Membership of a trade union, Philosophical beliefs, Political opinions, Religious beliefs or affiliations, Sexual orientation or practices.
|
|
Example(s)
|
- Name
- Personal identifiers (Customer)
- Indigenous status
- Health information
|
|
|
Records Authority
|
The National Archives of Australia (NAA) records authorities associated with the data.
|
|
Purpose
|
This attribute ensures disposal actions are clear and apparent, streamlining compliance with the relevant legal instrument governing keeping, transferring, or disposing of the data to enable compliance with the Privacy Code.
|
|
Additional comments
|
Please nominate the records authority or authorities associated with the data. The Administrative Functions Disposal Authority (AFDA) Express Version 2 contains a collection of general records authorities (GRAs) used across the agency.
For more information, refer to the NAA Records authorities or How to read and apply a Records Authority guidelines provided by the Records Management Helpdesk.
|
|
Obligation
|
Data Asset:
|
Mandatory
|
|
Data Exchange:
|
Mandatory
|
|
Data Transfer:
|
Not included
|
|
Controlled values
|
Record one or more values from the options provided - select the Plus (+) button to browse and add values. Where a desired value is not listed contact metadata.management.
|
|
Example(s)
|
- 2010/00715878 - Service Delivery (Centrelink)
|
|
|
Records Class No. and Disposal Action
|
The record class number and disposal action to which the data is subject under the relevant Records Authority.
|
|
Purpose
|
This attribute ensures disposal actions are clear and apparent, supporting compliance with disposal requirements.
|
|
|
Additional comments
|
Details of the disposal action that is to be taken on a particular class of record once a specified period of time has elapsed since a designated trigger event as documented in the relevant Records Authority.
Refer to “18.3 Disposal Action” within AGRkMS V2.2 (June 2015) for guidance.
For more information, refer to the NAA Records authorities or How to read and apply a Records Authority guidelines provided by the Records Management Helpdesk.
|
|
|
Obligation
|
Data Asset:
|
Mandatory
|
|
Data Exchange:
|
Mandatory
|
|
Data Transfer:
|
Not included
|
|
Controlled values
|
The class number and disposal action sourced from relevant records authority, formatted as:
- Class No. [nnnnn]. [disposal action text].
|
|
|
Example(s)
|
- Class No. 21925. Destroy 10 years after action completed
|
|
|
|
Access Instructions
|
The description of how users may seek access to the data.
|
|
Purpose
|
This attribute provides user guidance for how to gain access to the data.
|
|
Additional comments
|
The access instructions may include details such as:
- the restrictions or conditions placed on access to the data.
- any security resource or role required, e.g. via the ICT Security Portal (ISP).
- directory file path representing the location of the data.
|
|
Obligation
|
Data Asset:
|
Optional
|
|
Data Exchange:
|
Not included
|
|
Data Transfer:
|
Not included
|
|
Controlled values
|
At least one complete sentence.
|
|
Example(s)
|
Access is restricted to Services Australia employees who hold a baseline security clearance and can establish a ‘need to know’ justification. Request access via ICT Security Portal (ISP) for resource: SAS,123-ISO-ABC
|
|
|
Resource Type
|
The type of data being described, in terms of how the data is formatted.
|
|
Purpose
|
This attribute assists users to understand how the data is formatted.
|
|
|
Additional comments
|
The most common types of an item applicable are listed below with their definitions as per DublinCore and further granularity can be provided in Format.
- Collection: an aggregation of items. The term collection means that the resource is described as a group; its parts may be separately described and navigated.
- Dataset: structured information encoded in lists, tables, databases, etc., which will normally be in a format available for direct machine processing. For example: spreadsheets, databases, GIS data, midi data. Note that unstructured numbers and words would be considered as text.
- Image: the content is primarily symbolic visual representation other than text. For example: images and photographs of physical objects, paintings, prints, drawings, other images and graphics, animations and moving pictures, film, diagrams, maps, musical notation. Note that image may include both electronic and physical representations.
- Interactive resource: resources which require interaction from the user to be understood, executed, or experienced. For example: forms on web pages, applets, multimedia learning objects, virtual reality.
- Sound: a resource whose content is primarily audio or intended to be realised in audio. For example: music, speech, recorded sounds. This category includes musical notation, including score, which is unrealised in sound.
- Text: a resource whose content is primarily words for reading. For example - books, letters, dissertations, poems, newspapers, articles, archives of mailing lists. Note that facsimiles or images of texts are still of the genre text.
|
|
|
Obligation
|
Data Asset:
|
Mandatory
|
|
Data Exchange:
|
Not included
|
|
Data Transfer:
|
Mandatory
|
|
Controlled values
|
Select and record a single value from the options provided:
- Collection, Dataset, Event, Image, Interactive resource, Model, Physical object, Party, Place, Service, Software, Sound, Text.
A full list of resource type definitions can be found at Dublin Core – List of Resource Types
|
|
|
Example(s)
|
|
|
|
|
Format
|
The distribution format of the data.
|
|
Purpose
|
Provides certainty with data identification and assists users to assess suitability for use.
|
|
Additional comments
|
Supplements Resource Type to provide additional granularity to how the data is formatted
|
|
Obligation
|
Data Asset:
|
Mandatory
|
|
Data Exchange:
|
Not included
|
|
Data Transfer:
|
Mandatory
|
|
Controlled values
|
If the asset is distributed in multiple formats, please provide these as a comma-separated values.
Common format terms include, for example:
- PDF, DOCX, CSV, JSON, XLS, XLSX, DAT, XML, SQL, SAS, JPEG, JPG, PNG, BMP, GID, ZIP, TXT, HTML etc.
For structured data, provide the name and/or type of database. Common examples include:
- Apache Hive, Azure SQL, IBM DB2, M204, Microsoft SQL Server, MongoDB, Oracle Database, PostgreSQL, SAP HANA, Teradata.
|
|
Example(s)
|
|
|
|
File Size
|
The volume of digital storage needed by the data.
|
|
Purpose
|
This attribute provides data administrators with information to assist with managing potential storage issues and assists users with the logistics of requesting and storing data.
|
|
Additional comments
|
This field may not be relevant, for example, if your item is a data service or interactive resource. Where file size is constantly changing, provide an indicative size or an indicative size range for your item. This information may be sourced through the agency’s IT or data management department.
|
|
Obligation
|
Optional
|
|
Controlled values
|
- Digital assets: provide a number and units, for example 2KB, 4MB, 5GB, 1TB etc.
- Databases: provide the number of data tables stored in the catalog, for example 10 data tables in SQL.
|
|
Example(s)
|
|
|
|
Executive Data Steward
|
The executive data steward accountable for the data.
|
|
Purpose
|
The executive data attribute facilitates the unambiguous identification of the executive data stewards and provides stewards with insight into the data for which they are accountable.
|
|
Additional comments
|
The executive data steward is responsible for coordinating data governance at the branch level and managing data specifically relating to their position and authority, including the business outcomes their business units need to deliver.
Functions of an executive data steward include promoting compliance with legislation and information management policies and managing data related risks and issues.
A position and branch name are preferred to an individual’s contact because it is enduring and minimises the need to regularly update metadata records. Specific, individual stewardship details (including names) are recorded in the Data Stewards Register.
|
|
Obligation
|
Data Asset:
|
Mandatory
|
|
Data Exchange:
|
Mandatory
|
|
Data Transfer:
|
Not included
|
|
Controlled values
|
The executive data steward is recorded using the position and branch name, formatted as:
|
|
Example(s)
|
- NM Data Strategy and Governance Branch
|
|
|
Business Data Steward
|
The business data steward responsible for the data.
|
|
Purpose
|
The business data attribute facilitates the unambiguous identification of the business data stewards and provides stewards with insight into the data for which they are responsible.
|
|
Additional comments
|
The business data steward is responsible for the day-to-day management and use of an item from a business perspective. Business Data Stewards ensure all items are appropriately registered, approve access to an item and related information assets, and act as a point of contact for information about items they manage.
The business data steward holds the relevant authority to make decisions about an item, its data and management. The function is commonly fulfilled by an executive level employee but can also be an APS level employee with appropriate knowledge and decision-making authority.
A section name is preferred to an individual’s contact because it is enduring and minimises the need to regularly update metadata records. Specific, individual stewardship details (including names) are recorded in the Data Stewards Register.
|
|
Obligation
|
Data Asset:
|
Mandatory
|
|
Data Exchange:
|
Mandatory
|
|
Data Transfer:
|
Not included
|
|
Controlled values
|
The business data steward is recorded using the team or section name formatted as:
|
|
Example(s)
|
- Data Governance Operations Section
|
|
|
Technical Data Steward
|
The technical data steward, or data administrator, responsible for the creation and/or management of the data.
|
|
Purpose
|
The technical data steward attribute facilitates the unambiguous identification of the technical data stewards and provides clear identification of the data and analytics team responsible for their creation and management of data for which they are accountable.
|
|
Additional comments
|
Technical data stewards / data administrators may support business data stewards to create and manage an item, including the creation, definition and purpose of data, improving the quality of data and implementing access arrangements for authorised users. They may:
- Create and maintain data structures for reporting and analytics.
- Manage user access control methods based on advice from data stewards.
- Advise data stewards on technical issues related to an item.
- Install, upgrade and maintain data and analytics information systems.
- Maintain, create backups and restore data and information.
A branch and section name are preferred to an individual’s contact because it is enduring and minimises the need to regularly update metadata records. Specific, individual stewardship details (including names) are recorded in the Data Stewards Register.
|
|
Obligation
|
Data Asset:
|
Optional
|
|
Data Exchange:
|
Optional
|
|
Data Transfer:
|
Not included
|
|
Controlled values
|
The technical data steward is recorded using the branch and section name, formatted as:
- [Branch Name] – [Section Name]
|
|
Example(s)
|
- Business Intelligence and Performance Branch – Digital and Telephony Section
|
|
|
Technical Contact Point
|
An email address or a contact web form for users to request technical information about the production and/or management of the data.
|
|
Purpose
|
This attribute identifies technical subject matter experts who may be different to the business data steward and may be contacted for technical advice such as how an item is generated.
|
|
Additional comments
|
The technical contact point is recorded as a team or section that can provide additional information related to the data. The team or section shared mailbox address is preferred because it is generic and enduring, minimising the need to regularly update metadata records.
|
|
Obligation
|
Data Asset:
|
Optional
|
|
Data Exchange:
|
Optional
|
|
Data Transfer:
|
Not included
|
|
Controlled values
|
At least one valid email address or contact web form.
|
|
Example(s)
|
metadata.management@servicesaustralia.gov.au
|
|
|
Data Custodian
|
<p>The agency that is responsible for the data asset and has the authority for sharing and disclosure. The data custodian can differ from the publisher (see Publisher attribute). An agency may also be a data custodian under the <a href="https://www.legislation.gov.au/Details/C2022A00011">Data Availability and Transparency Act 2022</a> if:</p>
<ol>
<li>“[they are] a Commonwealth body; and</li>
<li>[are] not an excluded entity; and</li>
<li>either:;
<ul>
<li>controls public sector data (whether alone or jointly with another entity), including by having the right to deal with that data; or</li>
<li>has become the data custodian of output of a project in accordance with section 20F.”</li>
</ul>
</li>
</ol>
|
|
Purpose
|
Identifies the agency responsible for the data and has authority for sharing and disclosure.
|
|
Additional comments
|
Services Australia collects and manages a vast amount of customer data to administer payments and services for programs on behalf of policy departments,
- Policy departments are considered custodians of data collected for the administration on services and remain responsible for its sharing and disclosure.
- Services Australia is considered custodian of data collected for operational performance, agency workforce or corporate activities and remain responsible for its sharing and disclosure.
Arrangements or bilateral agreements may stipulate different or specific data custodian arrangements.
|
|
Obligation
|
Data Asset:
|
Conditional (Mandatory if data is collected on behalf of a policy agency)
|
|
Data Exchange:
|
Not included
|
|
Data Transfer:
|
Mandatory
|
|
Controlled values
|
Record one or more values from the options provided - select the Plus (+) button to browse and add values. Where a desired value is not listed contact metadata.management
A Data custodian value must be consistent with either the
|
|
Example(s)
|
- Department of Social Services
|
|
|
Publisher
|
The agency who has published the data, making it formally available for use.
|
|
Purpose
|
This attribute differentiates items originating within the agency from those sourced externally, e.g. through data exchange arrangements with other government agencies or departments.
|
|
Additional comments
|
The publisher is the agency that formally produces and is responsible for the release of the data and controls any future version release.
The Publisher may not be the Custodian (see Data Custodian attribute).
The default value may be your agency. If data is published by another agency, use a term from the Government Directory, Non-Government Organisation List or Research Organisation Register.
|
|
Obligation
|
Data Asset:
|
Optional
|
|
Data Exchange:
|
Not included
|
|
Data Transfer:
|
Not included
|
|
Controlled values
|
Select and record a single value from the options provided:
- Services Australia, Department of Social Services, Department of Health and Aged Care
Or contact metadata.management if the required organisation is not listed.
|
|
Example(s)
|
|
|
|
AGDC Status
|
<p>An indicator of the status of a record for contribution to the <a href="http://www.dataplace.gov.au/search/">Australian Government Data Catalogue</a> (AGDC).</p>
|
|
Purpose
|
This attribute assists with the identification of suitable records for contributing to the AGDC, including whether a record has already been contributed and should be maintained.
|
|
|
Additional comments
|
The AGDC Record Contribution guidelines identify the types of item records suitable to the AGDC and clarifies the roles and responsibilities, processes and technologies that enable this to occur.
|
|
|
Obligation
|
Mandatory
|
|
|
Controlled values
|
Select and record a single value from the options provided:
- Unsuitable (non-custodian): an external agency is responsible for an item and has the authority for sharing and disclosure. See Data Custodian attribute.
- Unsuitable (sensitivity): an item relates to sensitive business functions and, by making this information available, poses an unacceptable risk to the agency.
- Unsuitable (class/format): it is not the appropriate data asset class and/or it is a product to which the agency cannot provide access.
- Suitable: an item has been assessed as meeting the inclusion criteria for contribution to the Catalogue.
- Published: an item record has been published to the Catalogue.
|
|
|
Example(s)
|
Data Asset:
|
Unsuitable (sensitivity)
|
|
Data Exchange:
|
Unsuitable (class/format)
|
|
Data Transfer:
|
Unsuitable (class/format)
|
|
|
Exchange Transfer Direction
|
An indication of whether a data exchange transfer is inbound or outbound in relation to the agency recording the exchange.
|
|
Purpose
|
This attribute assists users identify whether a data transfer is providing data to a partner entity (outbound) or receiving data from a partner entity (inbound).
|
|
Additional comments
|
An exchange is comprised of one or more transfers, which can be either inbound or outbound in relation to the agency creating the record. If data is mutually exchanged, (both sent and received) this is recorded as two separate transfers.
|
|
Obligation
|
Data Asset:
|
Not included
|
|
Data Exchange:
|
Not included
|
|
Data Transfer:
|
Mandatory
|
|
Controlled values
|
Select and record a single value from the options provided:
- Inbound: Services Australia is receiving data from a partner entity.
- Outbound: Services Australia is providing data to a partner entity.
|
|
Example(s)
|
|
|
|
Exchange Delivery Method
|
The transmission method for data exchange transfer.
|
|
Purpose
|
This attribute identifies the specific transfer method used to provide or receive data.
|
|
Additional comments
|
The delivery methods are represented as either online or offline as defined below:
- Online Delivery Method: a digital method of communication or transfer.
- Offline Delivery Method: a physical method of communication or transfer.
|
|
Obligation
|
Data Asset:
|
Not included
|
|
Data Exchange:
|
Not included
|
|
Data Transfer:
|
Mandatory
|
|
Controlled values
|
Select and record a single value from the options provided:
- Online Delivery Methods: Application Programming Interface (API), ArcGIS Feature Server, ATO Data Transfer Protocol, Bluezone-File Transfer Protocol (FTP), Business Online Services, Business Portal, Cuba, Digital Gateway, ECXpert, External Data Exchange (EDX), Government to Government Server (GSO), HP Autonomy Process Automation, NZ Liaison Platform, IBM Sterling, Informatica, Line Printer Daemon, Managed File Transfer Facility, MQ Messaging, Open ID Connect, Optus Evolve, Organisation Online Mail, PGP, Protected Enclaves PAD, Public Key Infrastructure, Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP), Secure Network Interface Link, SIGBOX, Sterling Mail Transfer, Web Service Call, Xcomm, YSPBDOHA.
- Offline Delivery Methods: CD/DVD, Drop Box, Email, Encrypted USB, External Hard Drive, Facsimile, Hand Delivery, Non-Registered Post, Phone Call, Post, Registered Post
|
|
Example(s)
|
|
|
|
Data Audience
|
The intended audience, or consumers, of the data.
|
|
Purpose
|
This attribute identifies the intended audience of the data, as well as secondary consumers or recipients. This information facilitates stakeholder engagement and the identification of high-value / high-use data assets.
|
|
Obligation
|
Data Asset:
|
Optional
|
|
Data Exchange:
|
Not included
|
|
Data Transfer:
|
Not included
|
|
Controlled values
|
Record one or more values from the options provided - select the Plus (+) button to browse and add values. Where a desired value is not listed contact metadata.management.
- Group: a group within the agency, led by a deputy CEO, responsible for a generalised area of focus, reporting to the CEO and made up via a collection of divisions and branches.
- Division: a division within the agency, led by an SES GM, responsible for a collection of focus areas, reporting directly to a deputy CEO and made up via a collection of branches.
- Branch: a branch within the agency, led by an SES NM, responsible for a specific area of focus, reporting directly to a GM, and made up via a collection of business areas
|
|
Example(s)
|
- Group: Program Design, Division: Communities, Branch: Tailored Programs
|
|
|
Distribution Method
|
The method used to distribute or provide access to the data.
|
|
Purpose
|
Identify and manage distribution or access methods used for data assets across the agency.
|
|
Obligation
|
Data Asset:
|
Optional
|
|
Data Exchange:
|
Not included
|
|
Data Transfer:
|
Not included
|
|
Controlled values
|
Record one or more values from the options provided - select the Plus (+) button to browse and add values. Where a desired value is not listed contact metadata.management.
- Automated: reports are self-triggered and self-sending, requiring no staff intervention.
- Self Service: reports are open to users who can select and view the most current report.
- Static Report: reports will not update or change without another version being produced
- External: reports are sent outside of Services Australia.
- Branch Only: report visibility is limited to the branch responsible for its creation.
|
|
Example(s)
|
|
|
|
Physical Name
|
|
|
|
Services Australia Keywords (unused)
|
Word(s) or terms that describe the data asset subject matter.
|
Note: this field is unused as of 26/08/2024.
Purpose: Provides additional high-level information regarding asset content in a manner that facilitates discovery, linkage and descriptive analysis of data asset records.
Obligation: Optional
Additional comments: Keywords should be meaningful and relevant to the data asset. Select one or more keywords from the provided list. For a list of available keywords and definitions, refer to the the Data Asset Registration User Guide.
Controlled values: Select one or more keywords from the provided list - select the Plus (+) button to browse and add keywords. Where a desired keyword is not listed, contact metadata.management.
Example(s):
- Aged care services
- Application / claim
ONDC alignment: N/A |
|
Sensitive Data Type (unused)
|
The type of sensitivity of the data asset, where applicable.
|
Note: this field is unused as of 26/08/2024.
Purpose: To provide further detail about the type of sensitivity associated with the data.
Obligation: Conditional (mandatory if Security Classification is “OFFICIAL: Sensitive”)
Additional comments: If Security Classification has value “OFFICIAL: Sensitive”, provide the type of sensitivity. Provide one or more values from the list of options. For a definition of sensitive information refer to the Privacy and Secrecy intranet page. Record one or more values from the options provided - select the Plus (+) button to browse and add values
Controlled values: N/A (not sensitive), Personal privacy, Legal privilege (including commercial-in-confidence), Legislative secrecy
Example(s):
ONDC alignment: Sensitive Data (additional attribute) |
